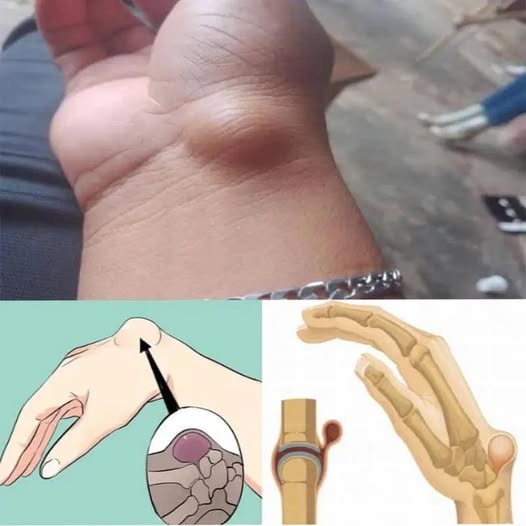
Effective Treatment Options for Wrist Ganglion Cysts
The choice of treatment depends on the cyst’s size, symptoms, and impact on daily activities. Here are the most common approaches:
Observation (Watch and Wait Approach)
If the cyst is small, painless, and doesn’t interfere with wrist function, doctors may recommend simply monitoring it. In some cases, ganglion cysts resolve on their own without intervention.
Immobilization
Wearing a wrist brace or splint can help reduce pressure on the joint, alleviate discomfort, and prevent the cyst from growing. This approach is particularly useful for cysts caused by repetitive strain.
Aspiration (Fluid Drainage)
A doctor can use a needle to drain the fluid from the cyst, providing temporary relief. However, this method has a high recurrence rate because it doesn’t remove the cyst’s sac.
Surgical Removal (Ganglion Excision)
For persistent or painful cysts that limit wrist function, surgery may be recommended. During the procedure, the entire cyst and its sac are removed, significantly reducing the likelihood of recurrence.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While ganglion cysts are typically benign, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional if:
-
The lump grows rapidly or changes in appearance.
-
You experience persistent pain or discomfort.
-
The cyst causes numbness, tingling, or weakness in the wrist or fingers.
-
Wrist movement becomes significantly restricted.
Final Thoughts: Managing Wrist Ganglion Cysts
Wrist ganglion cysts are usually harmless, but they can cause discomfort or functional limitations for some individuals. Non-invasive treatments like bracing and aspiration can provide relief, while surgical removal may be necessary for more severe or recurrent cases. If you suspect a ganglion cyst, consulting a doctor can help determine the best course of action for your specific situation.