The Peechia: What Your Little Red Stains Reveal About Your Health
Understanding petechiae: causes, symptoms and treatment
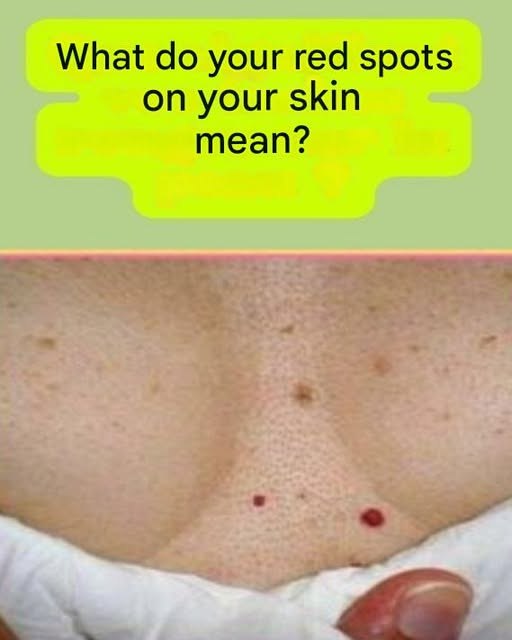
Petechiae are characteristic skin effects in the form of small red or purplish spots on the skin, usually the size of a pinhead. These particular dermatological signs usually result from micro-haemorrhages or subcutaneous blood leakage. Although often benign, these vascular lesions can sometimes be a sign revealing of more serious pathologies requiring specialized medical intervention. Let us examine this phenomenon in detail in detail.
Multifactorial origins of petechiae
The causes of petechiae are diverse and can be classified into several distinct categories:
Trauma or excessive pressure: The onset of petechiae may occur after a physical impact, bruise, or intense pressure on skin tissue, especially in repeated episodes of violent cough or vomiting.
Systemic infections: Certain infections of bacterial or viral origin, such as meningitis, scarlet fever or infectious mononucleosis, may trigger the occurrence of these characteristic bleeding lesions.
Hageological disorders: Petechiae may indicate blood clotting abnormalities or specific blood platelet conditions, such as thrombocytopenia – a medical condition characterised by a number of platelets in the blood.
Drug side effects: Many pharmacological treatments, particularly those affecting coagulation mechanisms such as therapeutic anticoagulants, may promote petechiae as an adverse reaction.Autoimmune diseases: Ailments such as systemic lupus erythematosus can cause these characteristic skin lesions in their clinical picture.
Malignant neoplasia: Petechiae may be a symptom of alerts of certain cancer diseases, such as leukaemia or malignant lymphoma.
Associated clinical events
Petechiae are presented as reddish dots or broken on the skin surface, usually painless and not raised. However, depending on the underlying aetiology, they may be accompanied by other revealing clinical signs:
Elevation of body temperature
Diffuse or localised painful symptoms
Increased haemorrhagic trend
Asthenia
Generalised rash
Indications for an urgent medical consultation
CONTINUE READING ON THE NEXT PAGE 🥰💕