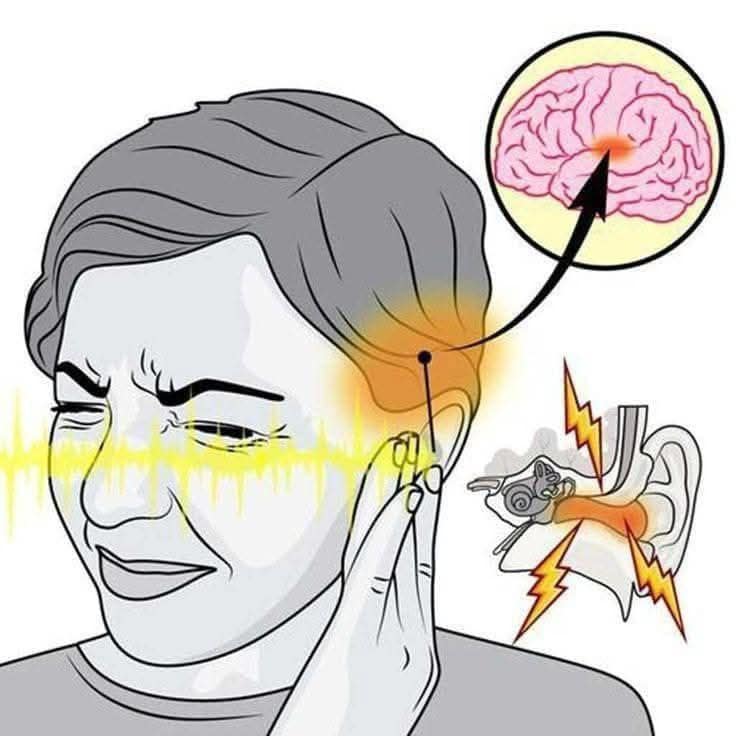
If you hear ringing in your ear, this is a sign that you will suffer from…
What Causes Tinnitus?
Tinnitus can arise from a variety of factors, including:
- Age-Related Hearing Loss (Presbycusis): As we age, the delicate hair cells in the inner ear that transmit sound to the brain can deteriorate, leading to tinnitus.
- Noise-Induced Hearing Loss: Prolonged exposure to loud noises—such as concerts, machinery, or headphones at high volumes—can damage the inner ear and cause ringing.
- Earwax Buildup: Excessive earwax can block the ear canal and irritate the eardrum, leading to tinnitus symptoms.
- Ear Infections or Blockages: Infections, fluid buildup, or other obstructions in the ear can contribute to ringing sounds.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as high doses of aspirin, diuretics, antibiotics, or chemotherapy drugs, can cause or worsen tinnitus.
- Underlying Health Conditions: Conditions like high blood pressure, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, or temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders may trigger tinnitus.
- Stress and Anxiety: Emotional stress can exacerbate tinnitus or make it more noticeable, creating a cycle of discomfort.
Is Ringing in the Ear a Sign of Something Serious?
While tinnitus is often harmless, persistent or worsening symptoms could indicate an underlying health issue that requires attention. If you experience any of the following, consult a healthcare professional immediately:
- Hearing Loss: Difficulty hearing conversations or sounds alongside the ringing.
- Dizziness or Vertigo: This could suggest an inner ear problem, such as Meniere’s disease.
- Pulsatile Tinnitus: A rhythmic ringing that matches your heartbeat, which might signal a vascular issue.
- Sudden Onset: If the ringing starts abruptly and is accompanied by pain, seek medical advice promptly.
How to Manage Tinnitus
CONTINUE READING ON THE NEXT PAGE 🥰💕